Technical requirements – Fundamentals of Cloud Architecture
Technical requirements
To fully engage with the content in this chapter on cloud computing architecture, you should have a basic understanding of computer systems, networking concepts, and information technology.
Additionally, the following technical requirements are recommended:
- Internet access: You should have a reliable internet connection to access online resources, references, and examples related to cloud computing.
- A computing device: A desktop computer, laptop, tablet, or smartphone with a modern web browser is necessary to read this chapter’s content and access any online materials.
- A web browser: The latest version of a modern web browser such as Google Chrome, Mozilla Firefox, Microsoft Edge, or Safari is recommended. This ensures compatibility and optimal viewing experience of web-based resources and interactive content.
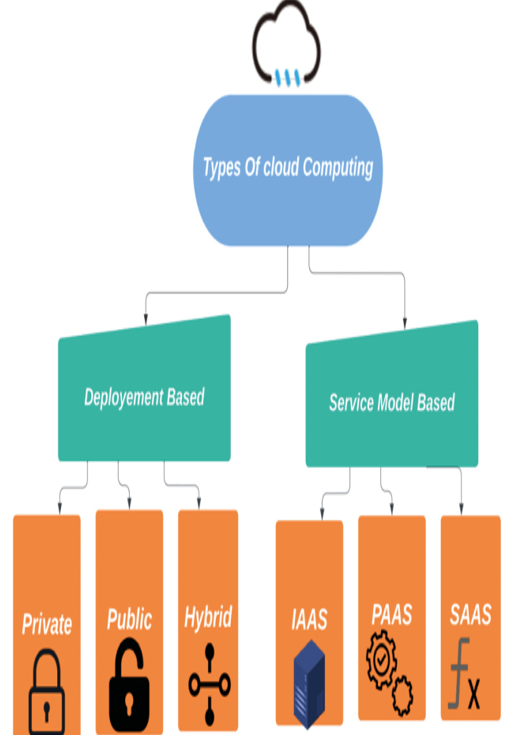
- Familiarity with cloud services: Some familiarity with cloud services and their basic functionalities will enhance your understanding of this chapter. This includes knowledge of cloud computing models such as Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS), Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS), and Software-as-a-Service (SaaS).
The history of cloud computing
Cloud computing has a rich history that has evolved over several decades. The concept of cloud computing dates back to the 1960s when computer scientists at MIT and Dartmouth College proposed the idea of a “utility computing” system that would allow users to access computing resources on demand.
In the 1970s, IBM introduced virtualization technology, which allowed multiple operating systems to run on a single mainframe computer. This technology enabled companies to consolidate their IT resources and reduce costs.
In the 1990s, the development of the World Wide Web and the rise of e-commerce led to the creation of web-based applications and services. This led to the development of early cloud computing platforms such as Salesforce, which provided customer relationship management (CRM) services over the internet.
In 2002, Amazon launched its web services division, offering cloud-based infrastructure services such as storage and computing power. This was followed by the launch of Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2) in 2006, which allowed users to rent computing capacity on demand.
In 2008, Google launched its cloud computing platform, Google App Engine, which allowed developers to build and run web applications on Google’s infrastructure.
Microsoft followed suit in 2010 with the launch of Windows Azure, which provided cloud-based services for building and deploying applications.
The growth of cloud computing has been fueled by advances in virtualization technology, which allows computing resources to be shared and used more efficiently. The development of cloud-based services and infrastructure has also made it easier for businesses to scale their IT resources up or down based on demand.
Today, cloud computing has become an integral part of many businesses, offering a range of benefits such as cost savings, scalability, flexibility, and improved collaboration. Cloud computing has also enabled the development of new technologies such as serverless computing, which allows developers to build and run applications without managing servers or infrastructure.
The main idea behind cloud computing was to provide a flexible and cost-effective way for users to access computing resources on demand. In the early days of computing, businesses and organizations had to invest in their IT infrastructure, including hardware, software, and networking equipment. This was expensive and often required a large upfront investment, which made it difficult for small and medium-sized businesses to compete with larger organizations.
Cloud computing was envisioned as a way to address this challenge by providing a shared pool of computing resources that could be accessed over the internet. This allowed businesses to pay only for the resources they needed, and to scale up or down as needed to meet changing demand.
In addition to cost savings, cloud computing was also seen as a way to improve the flexibility and agility of IT operations. By providing access to a shared pool of resources, cloud computing could enable businesses to quickly deploy new applications, scale up or down as needed, and respond to changing business needs more quickly than traditional IT infrastructure.
The thought behind cloud computing was to provide a more efficient, flexible, and cost-effective way for businesses to access the computing resources they need to operate and compete in today’s fast-paced digital economy.