Cloud computing today 2 – Fundamentals of Cloud Architecture
While cloud computing offers many benefits, it also comes with several challenges that must be addressed. One of the primary challenges is security, as cloud providers must ensure that users’ data is protected from unauthorized access or disclosure. Another challenge is vendor lock-in, as users may find it difficult to switch between cloud providers due to differences in technologies and architectures. Finally, there is the challenge of managing cloud costs, as users must carefully monitor and optimize their resource usage to avoid unexpected expenses.
Despite these challenges, cloud computing has become an essential part of the modern technology landscape, enabling businesses and individuals to access and use technology more efficiently and effectively than ever before.
The following figure depicts the general idea behind cloud computing:
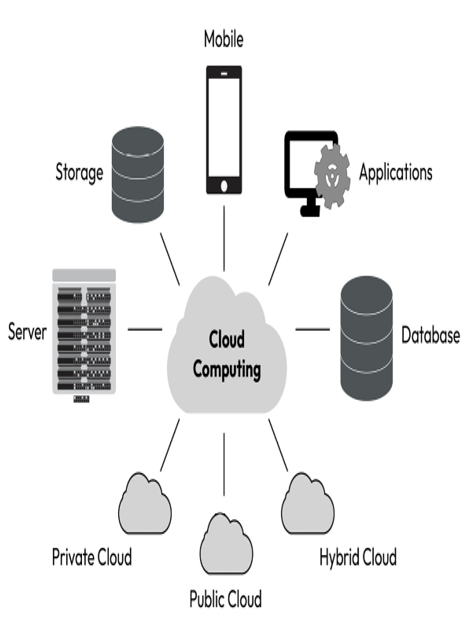
Figure 1.1 – The versatility and flexibility of cloud computing
This figure provides a concise overview of cloud computing, featuring key components such as databases, applications, compute, mobile devices, servers, and storage. It also highlights different cloud deployment models: public, private, and hybrid clouds. This figure visually represents these components and models, showcasing the interconnected nature of cloud computing.
Cloud computing has become an essential part of the modern technology landscape, enabling businesses and individuals to access and use technology more efficiently and effectively than ever before. With cloud computing, organizations can access technology resources as needed, without having to invest in and manage on-premises infrastructure. This allows companies to focus on their core business, while the cloud service provider manages the underlying technology. There are three main types of cloud computing: public cloud, private cloud, and hybrid cloud. The following figure depicts the basic design of cloud technology:
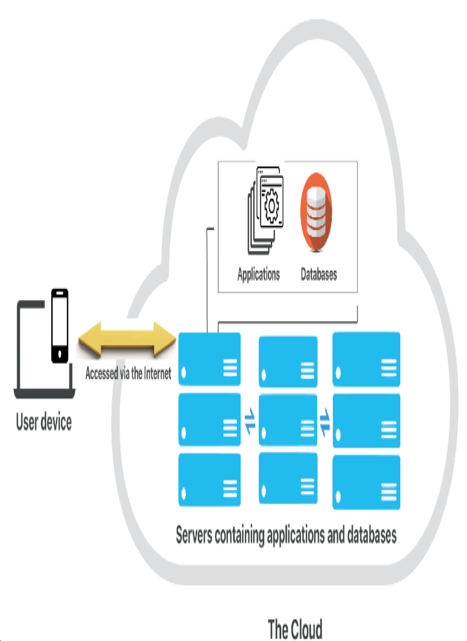
Figure 1.2 – Basic cloud design
The preceding figure depicts how basic cloud components reside within the cloud.
In this section, you learned about the origins and evolution of cloud computing, from time-sharing to the commercialization of services. You gained insights into key milestones, such as the development of virtualization technologies and the rise of utility computing.
Next, you explored the current state of cloud computing, including its models (IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS).
The next section dives into the foundational aspects of cloud architecture and provides you with a comprehensive understanding of its key components and design principles. It explores the fundamental building blocks of cloud architecture, including virtualization, resource pooling, and on-demand self-service.