Understanding cloud architecture 2 – Fundamentals of Cloud Architecture
- Cloud components: Cloud computing involves several components, such as VMs, containers, storage, networking, security, databases, and middleware. A cloud architect must have a clear understanding of each component’s capabilities and limitations to design and implement efficient and secure cloud solutions. Cloud computing encompasses various components that contribute to its functionality and infrastructure. Examples of these components include VMs, which allow you to run multiple operating systems on a single physical server, enabling efficient resource utilization. Containers, such as Docker and Kubernetes, offer lightweight, isolated environments for deploying and managing applications across different cloud environments. Storage services, such as Amazon S3 and Google Cloud Storage, provide scalable and reliable storage for data and files. Networking services, such as Amazon Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) and Azure Virtual Network, enable the creation of virtual networks to connect resources securely. Security services such as encryption, access control, and firewalls help protect data and applications. Cloud databases, such as Amazon RDS and Microsoft Azure SQL Database, provide scalable and managed database solutions. Middleware tools facilitate communication and integration between different software components and services in the cloud. These components collectively form the infrastructure and services that power cloud computing, offering organizations the flexibility, scalability, and convenience of cloud-based solutions.
- Cloud providers: Many cloud providers offer various cloud services and tools to build and deploy cloud solutions such as AWS, Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform (GCP). A cloud architect must have a deep understanding of these providers and their services to choose the right provider and services for their project. There are several prominent cloud providers in the market, each offering a wide range of services. AWS is a leading cloud provider, offering services such as Amazon EC2 for virtual servers, Amazon S3 for scalable storage, and Amazon RDS for managed databases. Microsoft Azure provides services such as Azure Virtual Machines, Azure Blob Storage, and Azure SQL Database. GCP offers services such as Google Compute Engine, Google Cloud Storage, and Google Cloud Spanner for distributed databases. Other notable cloud providers include IBM Cloud, with services such as IBM Cloud Virtual Servers and IBM Cloud Object Storage, and Oracle Cloud, offering services such as Oracle Compute and Oracle Database Cloud. These cloud providers offer a comprehensive suite of services, including compute, storage, databases, machine learning (ML), networking, and security, enabling organizations to build, deploy, and scale applications and infrastructure in the cloud. Figure 1.5 depicts the basic cloud architecture in AWS with key services such as VPC, EC2 (Compute), DynamoDB, and others:
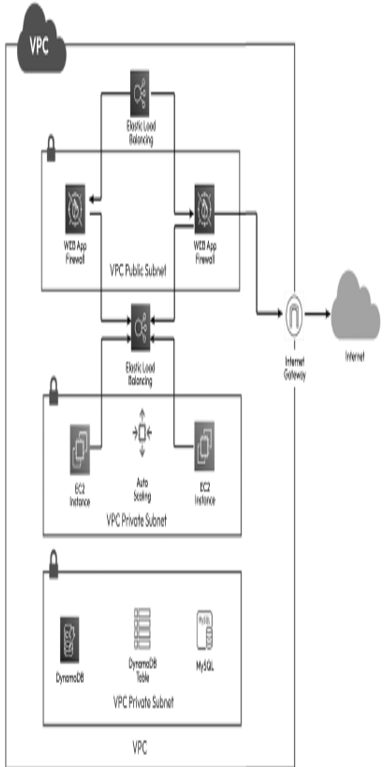
Figure 1.5 – Basic cloud architecture in AWS
- Cloud security: Cloud security is a critical component of cloud architecture. A cloud architect must design and implement security measures to protect the cloud infrastructure, data, and applications from unauthorized access, data breaches, and other security threats. Cloud security is a critical aspect of cloud computing, and several providers offer robust security services and solutions. One prominent cloud security provider is Cloudflare, which offers a range of security services such as DDoS protection, web application firewalls (WAFs), and content delivery networks (CDNs) to protect against malicious attacks. Another notable provider is Palo Alto Networks, which offers cloud security solutions such as Prisma Cloud, providing visibility, compliance, and threat protection across multi-cloud environments. Microsoft Azure also provides a comprehensive set of security services, including Azure Security Center, Azure Active Directory, and Azure Sentinel, offering identity management, threat detection, and security monitoring capabilities. AWS offers services such as AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM), AWS WAF, and AWS GuardDuty to help secure cloud environments. These cloud security providers and services play a crucial role in safeguarding data, applications, and infrastructure in the cloud, ensuring confidentiality, integrity, and availability of resources.
Overall, cloud architecture involves designing and managing cloud solutions that are scalable, reliable, secure, and cost-effective. A successful cloud architect must have a strong understanding of cloud technologies, architecture principles, and business needs to design and implement efficient and effective cloud solutions. In the upcoming section, we’ll explore the significant advantages and benefits that cloud architecture offers to organizations and individuals. Cloud computing has revolutionized the way we store, access, and process data, providing numerous advantages over traditional on-premises infrastructure.